What is Vercel AI SDK?
Vercel AI SDK is an open-source library developed by Vercel, which can be used for building AI-powered conversation streaming user interfaces.
With Vercel AI SDK, we can integrate various AI models from OpenAI, Hugging Face, LangChain, and Anthropic into the app to build a conversation stream similar to ChatGPT. Along with support for various LLMs (Language Models), Vercel AI SDK can also be used in frameworks like Next.js, Svelte, and Nuxt.
We can compare models and choose the one that fits our needs in the Vercel AI Playground.
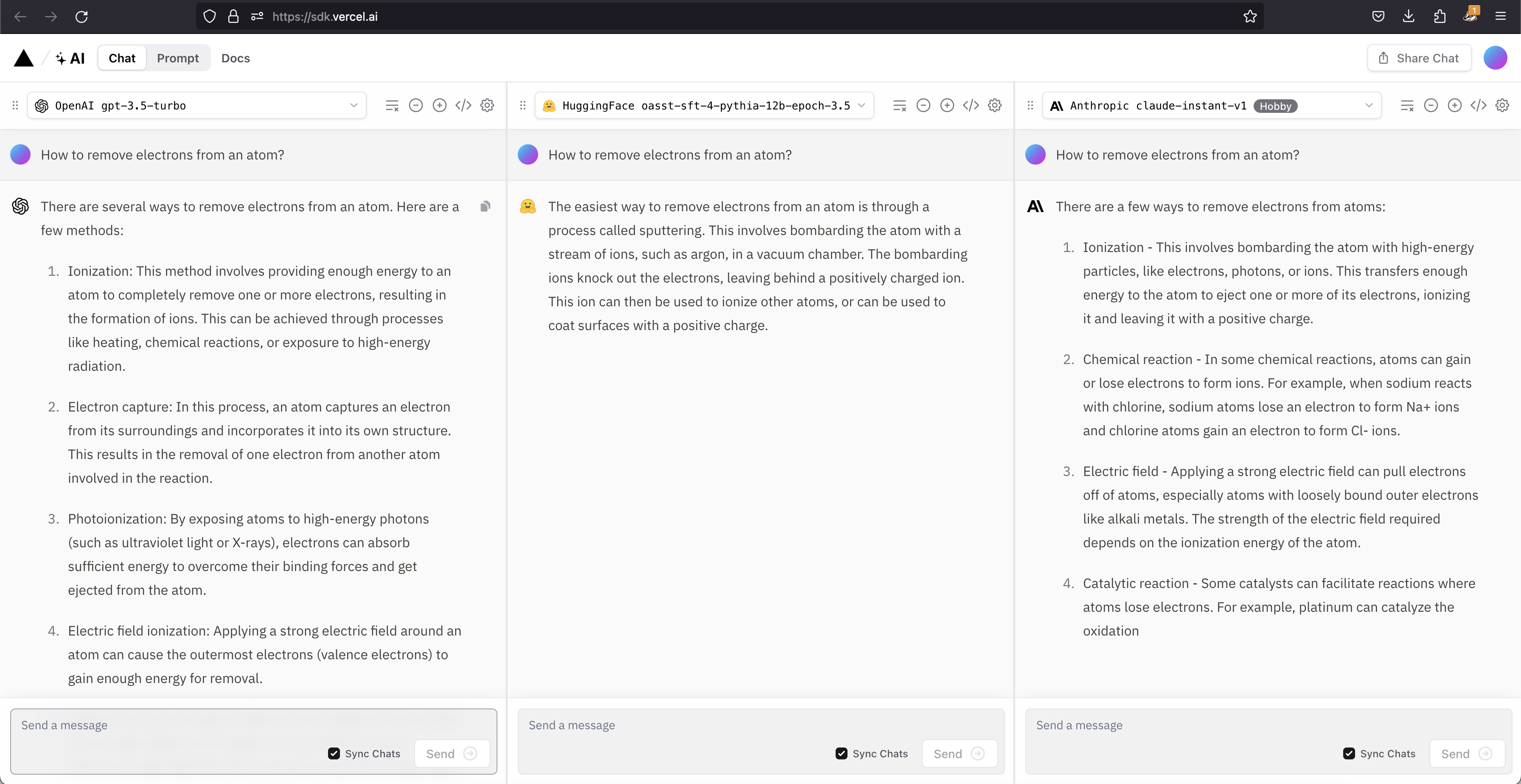
source: https://sdk.vercel.ai/
Available Hooks and Functions:
Before jumping into the implementation, let us understand the lifecycle and hooks provided in the Vercel AI SDK.
Vercel AI SDK come with two hooks useChat and useCompletion.
1) useChat:
The useChat hook allows us to stream the response from the AI provider. It manages the state of the input and updates the UI with the streamed response messages.
The options that can be passed to useChat are,
Lifecycle callbacks:
These lifecycle callbacks are optional and will be triggered based on the events.
- onResponse - This optional callback will be called when there is a response from the API endpoint.
- onFinish - This optional callback will be called when the stream ends.
- onError - This optional callback will be called when there is an error.
Other options:
- api - By default, the
/api/chatpath will be set. We can pass a different API endpoint if we want. - id - We can pass a unique ID for the chat. If not provided, a random one will be generated.
- initialInput - Initial text that will be pre-filled in the input field.
- initialMessages - A predefined chat message.
- headers - Headers that can be passed in this option.
- body - In addition to the message, we can pass a body object.
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit } = useChat()
2) useCompletion:
The useCompletion hook handles text completion based on the text input provided in the prompt. It also manages the state of the input and updates the UI with the streamed response messages.
The options that can be passed to useCompletion are:
Lifecycle callbacks:
These lifecycle callbacks are optional and will be triggered based on the events.
- onResponse - This optional callback will be called when there is a response from the API endpoint.
- onFinish - This optional callback will be called when the stream ends.
- onError - This optional callback will be called when there is an error.
Other options:
- api - By default, the
/api/completionpath will be set. We can pass a different API endpoint if we want. - id - We can pass a unique ID for the completion. If not provided, a random one will be generated.
- initialInput - Initial text that will be pre-filled in the input field.
- initialCompletion - A predefined completion message.
- headers - Headers that can be passed in this option.
- body - In addition to the message, we can pass a body object.
const {
completion,
input,
stop,
isLoading,
handleInputChange,
handleSubmit
} = useCompletion({
api: '/api/completion'
})
AIStream:
AIStream is a helper function for creating a readable stream response. This handles AI reponse stream and works with useChat and useCompletion functions.
OpenAIStream:
OpenAIStream is a utility function that transforms the response from OpenAI into a readable stream.
There are other AI stream utility functions available, such as HuggingFaceStream, AnthropicStream, and LangChainStream, but for this blog, we will focus on OpenAI.
To obtain a readable stream, we need to pass the response from the openai.createCompletion or openai.createChatCompletion functions.
It is compatible with various OpenAI models, including:
- The gpt-4 model, which is optimized for complex tasks and chat functionality.
- The gpt-3.5 model, which is the most capable model specifically optimized for chat.
- The text-davinci-003 model, which excels at language tasks with better quality, longer output, and consistent instructions.
- The text-davinci-002 model, which has similar capabilities to text-davinci-003 but was trained with supervised fine-tuning.
To enable steaming reponse message, it is recommended to use the openai-edge package, which allows steaming chats and completions response.
Parameters:
- res - This is a required parameter where we pass the response from the
createCompletionorcreateChatCompletionfunction. - cb? - This is an optional parameter where we can pass a callback function.
const response = await openai.createChatCompletion({
model: 'gpt-4',
stream: true,
messages
})
// Transform the response into a readable stream
const stream = OpenAIStream(response)
StreamingTextResponse:
StreamingTextResponse is a utility class that enables the generation of a readable stream containing text as an HTTP response.
It will automatically set 200 status code and content type header to 'text/plain; charset=utf-8'.
const stream = OpenAIStream(response);
// Respond with the stream
return new StreamingTextResponse(stream);
Implementation
In this post, we will be utilizing the OpenAI model with the help of OpenAIStream, which can be used with both the chat and completion models.
The Vercel AI SDK provides templates for all supported frameworks. For this post, we will be using the Next.js OpenAI starter repository.
1) Install pnpm package manager
npm install -g pnpm
2) Create the Next.js app:
pnpm create next-app --example https://github.com/vercel-labs/ai/tree/main/examples/next-openai next-openai-app
3) Create an OpenAI account if you don’t have one already.
4) In OpenAI Dashboard create API key and copy it.
5) Set the environment variable by using the export command in the terminal or by creating a new file called .env.local and pasting the API key there
OPENAI_API_KEY=xxxxxxx
6) Install dependencies by running pnpm install
7) Run the development server by running pnpm dev
The template provided already includes a chat interface that supports streaming, similar to ChatGPT. However, to implement the Vercel AI SDK in a Next.js app, we need to add an App route file and a Page file.
Chat model:
Creating an App route:
To implement the chat model, create a folder api/chat in the app directory and within the app/api/chat folder, create a file named route.ts. This file will contain the route definitions for the chat API.
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { Configuration, OpenAIApi } from 'openai-edge'
import { OpenAIStream, StreamingTextResponse } from 'ai'
// Create an OpenAI API client (that's edge friendly!)
const config = new Configuration({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY
})
const openai = new OpenAIApi(config)
// IMPORTANT! Set the runtime to edge
export const runtime = 'edge'
export async function POST(req: Request) {
// Extract the `prompt` from the body of the request
const { messages } = await req.json()
// Ask OpenAI for a streaming chat completion given the prompt
const response = await openai.createChatCompletion({
model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
stream: true,
messages: messages.map((message: any) => ({
content: message.content,
role: message.role
}))
})
// Convert the response into a friendly text-stream
const stream = OpenAIStream(response)
// Respond with the stream
return new StreamingTextResponse(stream)
}In the above code, we have used the OpenAI chat model. Using OpenAIStream and StreamingTextResponse, we can transform the response into readable stream text in the HTTP response.
We are using gpt-3.5-turbo model for chat. We are providing the user instruction in the message parameter which the AI agent will use to generate a response. The message parameter consists of an array of objects, with each object containing the content and role properties.
The content property holds the text of the message, while the role property specifies the role of the message, indicating whether it is from the user or the AI agent.
Creating a page route:
In the app directory create a page.tsx file in the app directory.
// app/api/chat/page.tsx
'use client'
import { useCompletion, useChat } from 'ai/react';
export default function Chat() {
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit } = useChat()
return (
<div className="flex flex-col w-full max-w-md py-24 mx-auto stretch text-black">
{messages.length > 0
? messages.map(m => (
<div key={m.id} className="whitespace-pre-wrap">
{m.role === 'user' ? 'User: ' : 'AI: '}
{m.content}
</div>
))
: null}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
className="fixed bottom-0 w-full max-w-md p-2 mb-8 border border-gray-300 rounded shadow-xl text-black"
value={input}
placeholder="Say something..."
onChange={handleInputChange}
/>
</form>
</div>
)
}In the above code, the useChat hook will make a request to the default API endpoint /api/chat, and the response will be set in the messages state as an array.
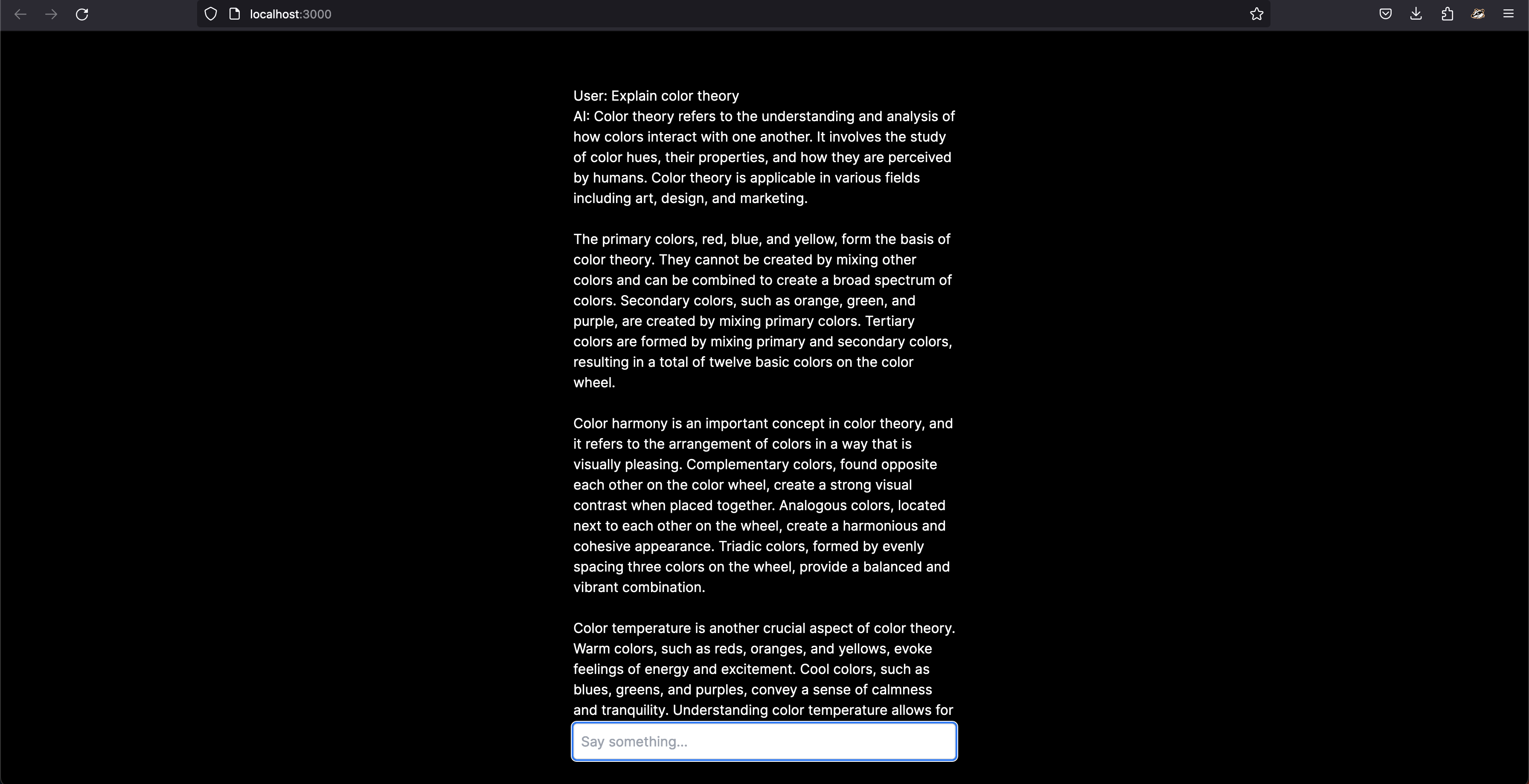
Here is a sandbox of the chatbot,
Completion model:
We can use the same chat template and make some changes to the page.tsx file and create a new endpoint for completion.
Creating an App route:
For the completion model, create a folder api/completion in the app directory and within the app/api/completion folder, create a file named route.ts. This file will contain the route definitions for the completion API.
// app/api/completion/route.ts
import { Configuration, OpenAIApi } from 'openai-edge';
import { OpenAIStream, StreamingTextResponse } from 'ai';
// Create an OpenAI API client (that's edge friendly!)
const config = new Configuration({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
const openai = new OpenAIApi(config);
// Set the runtime to edge for best performance
export const runtime = 'edge';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { prompt } = await req.json();
// Ask OpenAI for a streaming completion given the prompt
const response = await openai.createCompletion({
model: 'text-davinci-003',
stream: true,
temperature: 0.6,
prompt: `Convert the given code to ruby.
User: ${prompt}
Agent:`
});
// Convert the response into a friendly text-stream
const stream = OpenAIStream(response);
// Respond with the stream
return new StreamingTextResponse(stream);
}In the above code, we have used OpenAI completion model, using OpenAIStream and StreamingTextResponse, we can transform the repsonse into readable stream text in HTTP response.
We are using text-davinci-003 model for completion. By providing prompt we can give specific instructions to the AI Agent and guide it to perform a particular task.
Creating a Page route:
In the app directory create a page.tsx file in the app directory.
'use client'
import { useCompletion, useChat } from 'ai/react';
export default function ConvertToRuby() {
const { completion, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit } = useCompletion({api: '/api/completion'});
return (
<div className="mx-auto w-full max-w-md py-24 flex flex-col stretch">
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
className="fixed w-full max-w-md bottom-0 border border-gray-300 rounded mb-8 shadow-xl p-2 text-black"
value={input}
placeholder="Conver to Ruby..."
onChange={handleInputChange}
/>
</form>
<div className="whitespace-pre-wrap my-6">{completion}</div>
</div>
);
}In the above code, the useCompletion hook makes a request to the API endpoint /api/completion, and the response is set in the completion state.

Here is a sandbox of the conversation model,
